LASER WELDING
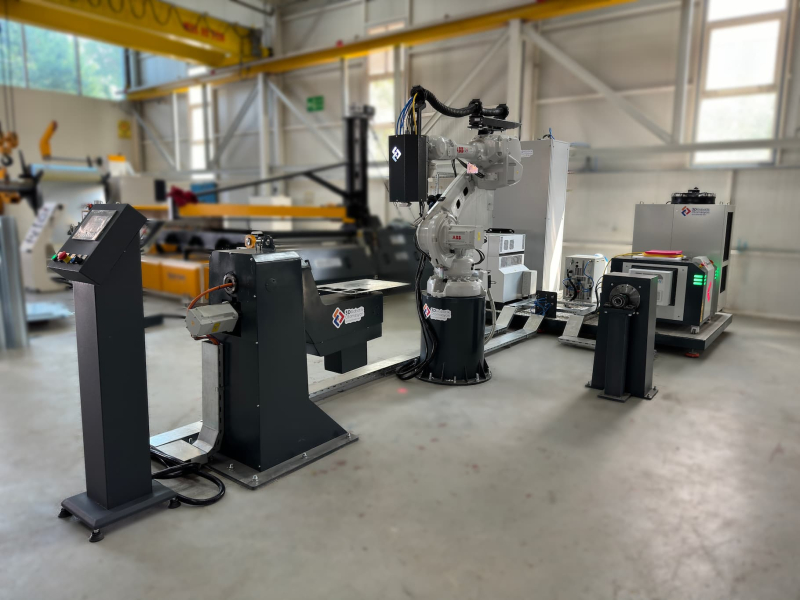

Step-by-Step Laser Welding Process
-
Laser Beam Generation
The fundamental principle of laser welding begins with generating a laser beam. The laser is typically created within a resonator and focused into a thin, high-energy beam. This laser beam can be produced from different sources such as fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, or Nd:YAG lasers. -
Directing the Laser Beam
The generated laser beam is focused and directed onto the material to be welded using special mirrors and lenses. Proper focusing of the laser beam ensures a high energy density, causing the material’s surface to rapidly heat and melt. -
Melting the Material
When the laser beam hits the material, the light energy is converted into heat. This heat causes the surface of the material to begin melting. The melted area is where the weld seam between the materials will form. -
Joining and Cooling
The melted material fuses the two parts together. As the laser beam moves along, the molten material quickly cools, creating a strong bond between the two parts. The cooling process is very fast, resulting in minimal material deformation. -
Thin and Durable Welds
Laser welding produces extremely thin and smooth weld seams with minimal material loss. These welds are more durable compared to traditional welding methods and provide significant advantages for thin materials.
Characteristics of Laser Welding
-
High Precision
The ability to focus the laser beam allows only the targeted area of the material to be melted. This ensures that the rest of the material remains unaffected, enabling precise and delicate welds. -
Fast Processing
Laser welding is faster compared to other welding methods. This speed is particularly advantageous in mass production processes. -
Material Versatility
Laser welding can be used on a variety of metals and even some plastics. Materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium are suitable for laser welding.
Applications of Laser Welding Technology
Laser welding technology is used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and metalworking. Precision, speed, and minimal impact on the material make laser welding an ideal choice for critical applications.
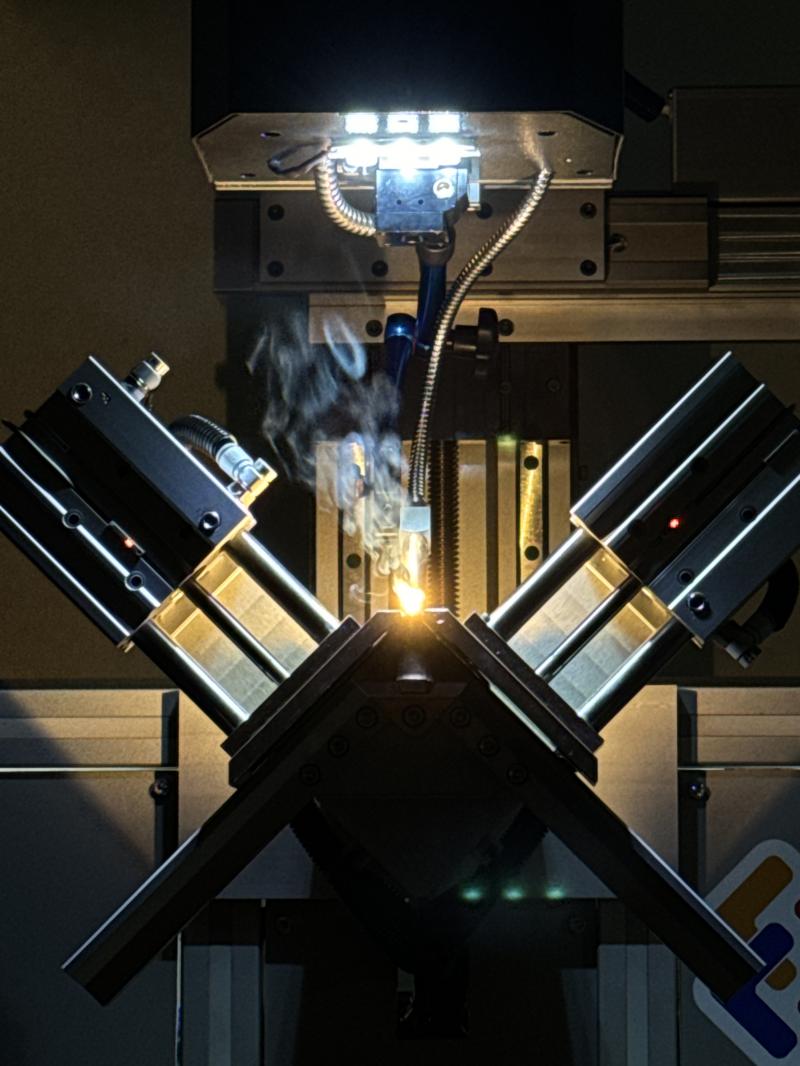
-
High Precision
Laser welding offers the ability to work with high precision on small and delicate parts, making it highly advantageous in industries requiring accuracy. -
Reduced Heat Effect
Laser welding affects only the targeted welding area, minimizing material deformation and limiting the thermal impact on the surrounding material. -
High Speed
Compared to other welding methods, laser welding is much faster, allowing for time savings in mass production processes. -
Clean and Aesthetic Welds
Laser welding creates very clean and smooth welds on materials, which is especially preferred in projects where visual quality is crucial. -
Minimal Material Loss
During laser welding, material loss is significantly reduced, which lowers costs and increases efficiency. -
Compatibility with Various Materials
Laser welding can be used on a wide range of materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and even some plastics. -
Automation Capability
Laser welding machines can be integrated with robots for fully automated production lines, reducing human error and speeding up processes.
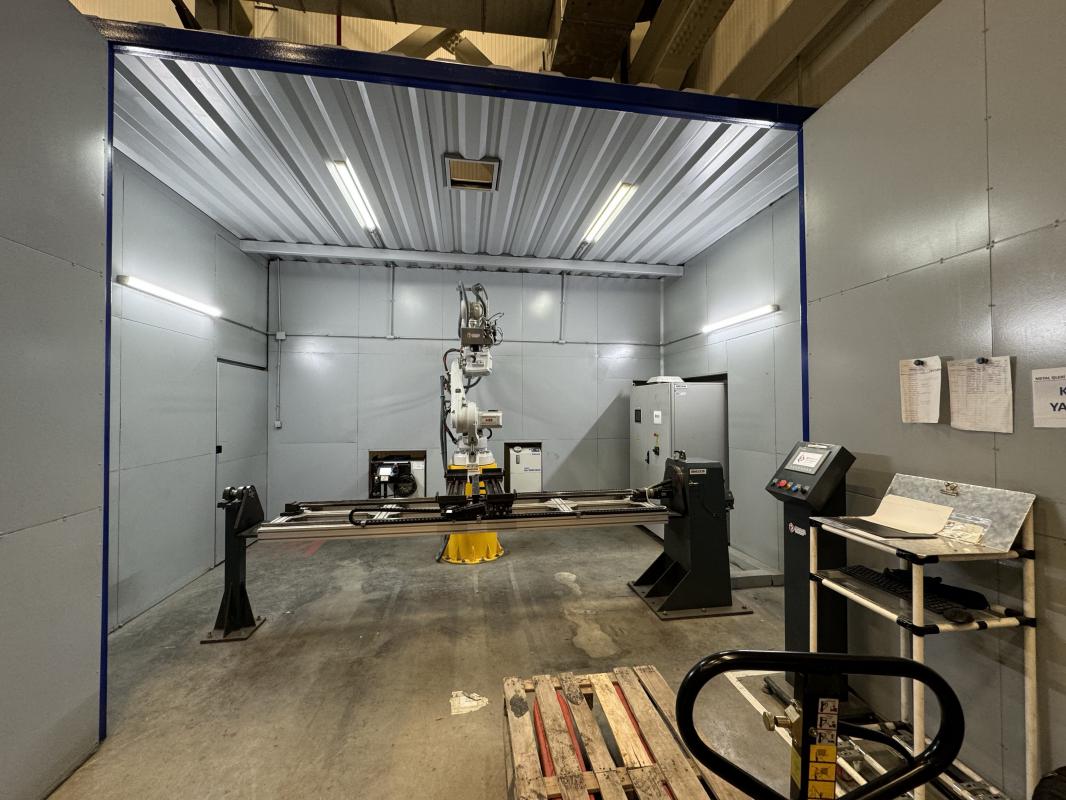

-
Automotive Industry
Laser welding is used in the production of automobile parts, especially for joining thin metal sheets. It is applied in critical areas such as engine components, chassis, and body panels. -
Aerospace Industry
In the production of aircraft and spacecraft parts, laser welding is preferred for the joining of lightweight and durable materials. It is used in applications requiring high precision and strength. -
Electronics and Microelectronics
Laser welding plays a crucial role in joining small and delicate components. It is an ideal method for circuit boards, microchips, and other electronic devices. -
Medical Devices
Laser welding is used in the production of medical devices by welding biocompatible metals like stainless steel and titanium. Stents, prosthetics, and surgical tools are manufactured using this technology. -
Metalworking and Manufacturing
In the metal industry, laser welding is widely used for the production of sheet metal, pipes, and other metal structures. It provides high durability with minimal deformation. -
Jewelry and Watch Industry
Laser welding is ideal for creating fine and delicate weld seams in the production of jewelry and watches, where small and detailed components need to be joined. -
Energy Sector
Laser welding is preferred in the assembly of components used in energy production, such as solar panels and batteries.
What Materials Can Be Welded with Laser Welding?
Laser welding can be used on a variety of metals and materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, nickel alloys, carbon steel, and some plastics. It is particularly efficient on thin and delicate materials.
Is Laser Welding Better Than Traditional Welding Methods?
Laser welding is more precise and faster compared to traditional welding methods. It also causes less material deformation and creates much finer seams. However, both methods have their own advantages depending on the nature of the application.
Does High Heat Damage the Material During Laser Welding?
Laser welding focuses heat only on the targeted area, so the heat effect is limited. Most of the material remains unaffected, making this process highly advantageous for delicate materials.
Which Industries Use Laser Welding?
Laser welding is used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, metalworking, jewelry, and watchmaking. The precision, speed, and versatility of laser welding make it a popular choice in these sectors.
Can Laser Welding Machines Be Automated?
Yes, laser welding machines can be integrated with robots for use in fully automated production lines. This minimizes human error and increases production speed.
Is Laser Welding Expensive?
The initial cost may be higher than traditional methods, but the advantages of speed, efficiency, and material savings can balance out the cost in the long run. Additionally, laser welding can be integrated into automated systems, reducing labor costs.
